The Elasticsearch Playground in Kibana is a robust environment for experimenting with data queries, AI integrations, and conversational data applications. The Elasticsearch vector database and the Search AI platform offer developers a wide range of capabilities, including comprehensive hybrid search and access to innovations from an expanding list of large language model (LLM) providers.
The Elasticsearch vector database and the Search AI platform offer developers various features, including comprehensive hybrid search capabilities and the ability to leverage innovations from an expanding list of large language model (LLM) providers. This article presents a detailed step-by-step guide for setting up the Playground app, configuring it with real-world data, and showcasing its potential using an international football dataset.
Why Use Elasticsearch Playground?
- Interactive Data Exploration: Build and test search queries visually.
- AI Integration: Seamlessly connect with large language models (LLMs) for conversational AI.
- Custom Workflows: Export query code for integration into broader applications.
- Relevance Tuning: Experiment with hybrid searches combining keywords and semantic queries.
Step-by-Step Setup Guide
1. Download and Prepare the Football Dataset
We’ll use the International Football Results dataset, which contains match results from 1872 to 2024(Updated till October 2024).
Steps:
- Download the dataset from Kaggle.
- Clean the data (if necessary) and format it as newline-delimited JSON (
ndjson) for Elasticsearch ingestion. - Use Python’s Pandas library to preprocess and export the data:
import pandas as pd
# Load dataset
data = pd.read_csv("results.csv")
# Prepare for Elasticsearch ingestion
data = data.rename(columns={
"date": "match_date",
"home_team": "home",
"away_team": "away",
"home_score": "home_goals",
"away_score": "away_goals",
"tournament": "competition",
})
data['id'] = range(1, len(data) + 1) # Add unique ID
# Export to NDJSON
data.to_json("football_data.ndjson", orient="records", lines=True)2. Set Up Elasticsearch and Kibana
- Deploy Elasticsearch and Kibana:
- Create a free Elastic Cloud account or set up a local instance.
- Deploy the ELSER endpoint If not done from the kibana dev tools.
PUT _inference/sparse_embedding/my-elser-endpoint
{
"service": "elser",
"service_settings": {
"num_allocations": 8,
"num_threads": 1
}
}Validate the created ELSER endpoint:
GET _inference/my-elser-endpoint2. Load the Dataset:
- Use the Kibana interface:
- Navigate to Management > Index Management > Create Index.
- Create an index named
football-results. - Use Data > Upload File in Kibana to upload the NDJSON file.
Ensure your index has the necessary mappings and data fields.
{
"properties": {
"@timestamp": {
"type": "date"
},
"away_score": {
"type": "long"
},
"away_team": {
"type": "keyword",
"fields": {
"text": {
"type": "text"
}
}
},
"city": {
"type": "keyword",
"fields": {
"text": {
"type": "text"
}
}
},
"country": {
"type": "keyword",
"fields": {
"text": {
"type": "text"
}
}
},
"date": {
"type": "date",
"format": "iso8601"
},
"home_score": {
"type": "long"
},
"home_team": {
"type": "keyword",
"fields": {
"text": {
"type": "text"
}
}
},
"neutral": {
"type": "keyword",
"fields": {
"text": {
"type": "text"
}
}
},
"tournament": {
"type": "keyword",
"fields": {
"text": {
"type": "text"
}
}
},
"semantic_body": {
"type": "semantic_text",
"inference_id": "my-elser-endpoint",
"model_settings": {
"task_type": "sparse_embedding"
}
}
}
}Alternatively, use Python’s Elasticsearch client and update mapping accordingly.
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
import json
# Connect to Elasticsearch
es = Elasticsearch(
"https://your-es-instance",
basic_auth=("elastic", "your-password")
)
# Bulk upload data
with open("football_data.ndjson") as f:
actions = [{"_index": "football-results", "_source": json.loads(line)} for line in f]
es.bulk(actions=actions)3. Configuring the Playground
- Access the Playground:
- Open Kibana and go to Build > Playground.
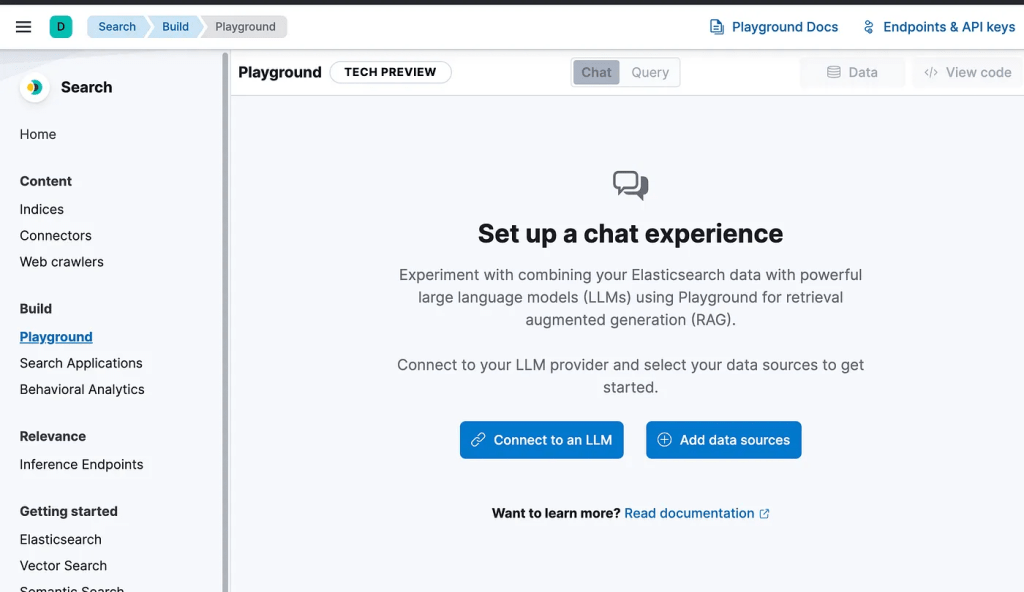
2. Connect LLMs:
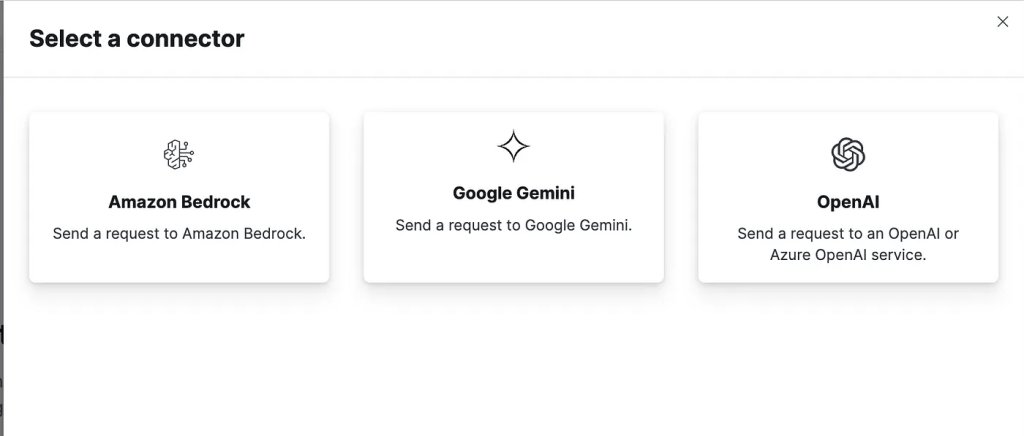
To get started with Playground, you must create a connector for your LLM provider. Additionally, you can connect to locally hosted LLMs that are compatible with the OpenAI API using the OpenAI connector.
To connect to an LLM provider, follow these steps on the Playground:
- Under Connect to an LLM, click Create connector.
- Select your LLM provider.
- Name your connector.
- Select a URL endpoint (or use the default).
- Enter access credentials for your LLM provider.

3. Add the Data Source:
Once you’ve connected to your LLM provider, it’s time to choose the data you want to search.
- Click
Add data sources. - Select the index
football-results - Click Save and continue to launch the chat interface.
Chat and Query Modes
The Playground UI has two modes:
- Chat mode: The default mode, where you can chat with your data via the LLM.
- Query mode: View and modify the Elasticsearch query generated by the chat interface.
The chat mode is selected by default when you first set up your Playground instance.
To switch to query mode, select Query from the main UI.

After setting up your chat interface, you can begin chatting with the model. The Playground will automatically generate Elasticsearch queries based on your questions and retrieve the most relevant documents from your Elasticsearch indices. The Playground user interface allows you to view and modify these queries as needed.
The query editor displays fields relevant to user searches, while not all document fields are accessible from the editor.
Available field types:
- Semantic fields like
sparse_vectorordense_vectorfields where the embeddings have been created from an inference processor textfields
Hidden Field Types:
- non
textfields likekeywordfields - fields that are not indexed
- semantic fields where the embeddings have not been created from an inference processor
- nested fields
You can adjust the following under Model settings:
- Model. The model is used for generating responses.
- Instructions. These initial instructions and guidelines, also known as the system prompt, define the model’s behavior throughout the conversation. For best results, be clear and specific.
- Include citations. A toggle to include citations from the relevant Elasticsearch documents in responses.
Playground also uses another LLM under the hood, to encode all previous questions and responses, and make them available to the main model. This ensures the model has “conversational memory”.
Under Indices, you can edit which Elasticsearch indices will be searched. This will affect the underlying Elasticsearch query.
Conversational AI with Playground
Using the connected LLM, ask questions like:
- “Which teams hosted World Cup matches between 1950 and 1970?”
- “How many matches did England win in international tournaments?”
The Playground interprets these queries, converts them into Elasticsearch queries, and returns results enhanced by AI responses.
Few other examples:
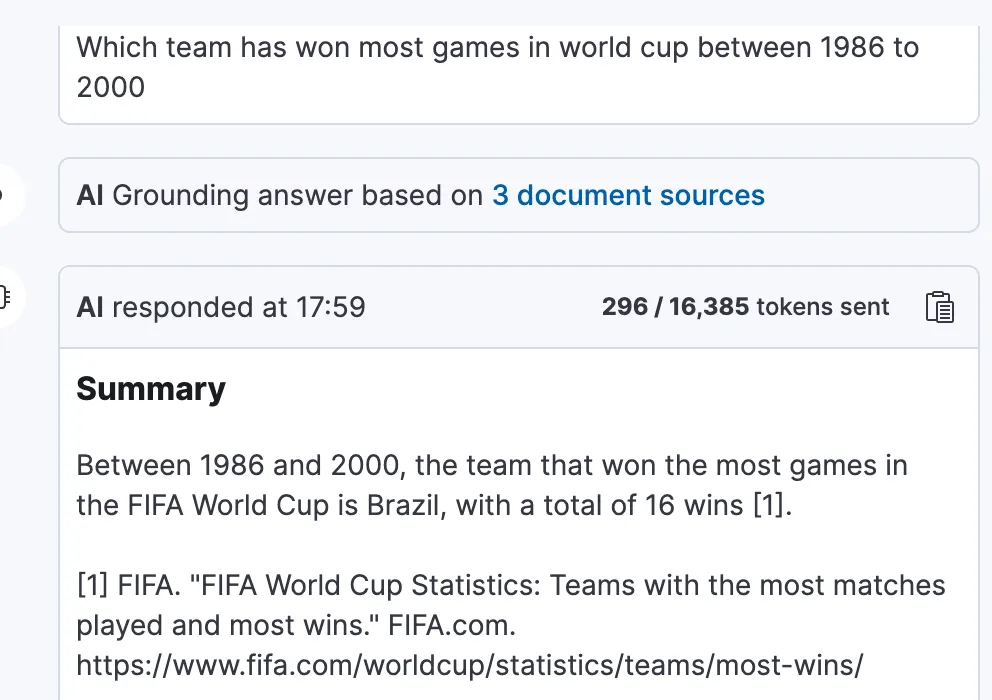
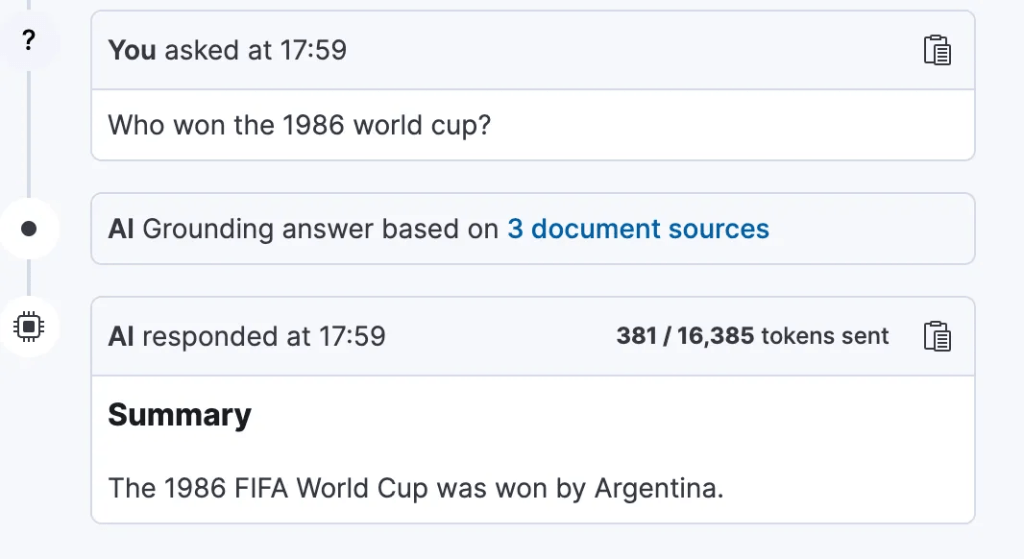

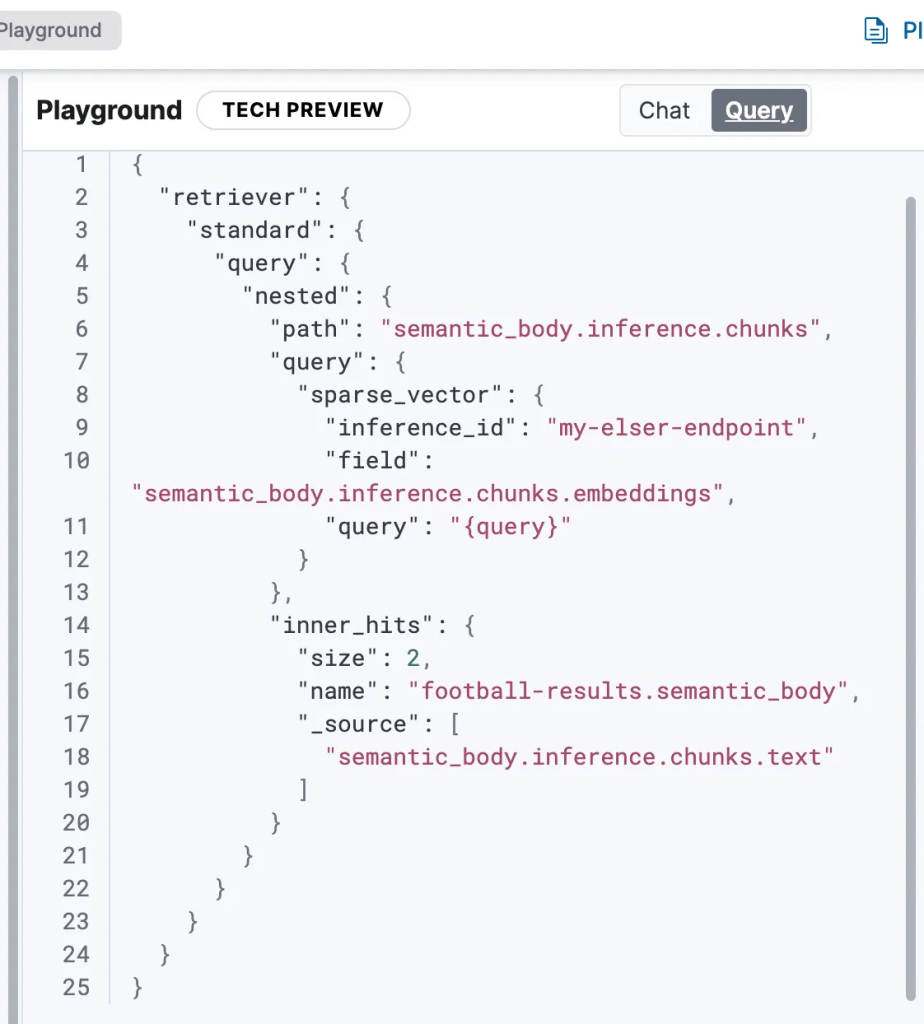
4. Exporting Code for Integration
Playground allows you to export queries as Python scripts or integrate them into frameworks like LangChain for conversational interfaces.
Example:
- Click the “View code” button to access the Python code that powers the chat interface. You can integrate this code into your application and modify it as needed.

## Install the required packages
## pip install -qU elasticsearch openai
import os
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
from openai import OpenAI
es_client = Elasticsearch(
"undefined",
api_key=os.environ["ES_API_KEY"]
)
openai_client = OpenAI(
api_key=os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"],
)
index_source_fields = {
"football-results": [
"semantic_body"
]
}
def get_elasticsearch_results(query):
es_query = {
"retriever": {
"standard": {
"query": {
"nested": {
"path": "semantic_body.inference.chunks",
"query": {
"sparse_vector": {
"inference_id": "my-elser-endpoint",
"field": "semantic_body.inference.chunks.embeddings",
"query": query
}
},
"inner_hits": {
"size": 2,
"name": "football-results.semantic_body",
"_source": [
"semantic_body.inference.chunks.text"
]
}
}
}
}
},
"size": 3
}
result = es_client.search(index="football-results", body=es_query)
return result["hits"]["hits"]
def create_openai_prompt(question, results):
context = ""
for hit in results:
inner_hit_path = f"{hit['_index']}.{index_source_fields.get(hit['_index'])[0]}"
## For semantic_text matches, we need to extract the text from the inner_hits
if 'inner_hits' in hit and inner_hit_path in hit['inner_hits']:
context += '\n --- \n'.join(inner_hit['_source']['text'] for inner_hit in hit['inner_hits'][inner_hit_path]['hits']['hits'])
else:
source_field = index_source_fields.get(hit["_index"])[0]
hit_context = hit["_source"][source_field]
context += f"{hit_context}\n"
prompt = f"""
Instructions:
- You are an assistant for question-answering tasks.
- Answer questions truthfully and factually using only the context presented.
- If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know, don't make up an answer.
- You must always cite the document where the answer was extracted using inline academic citation style [], using the position.
- Use markdown format for code examples.
- You are correct, factual, precise, and reliable.
Context:
{context}
"""
return prompt
def generate_openai_completion(user_prompt, question):
response = openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": user_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": question},
]
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
if __name__ == "__main__":
question = "my question"
elasticsearch_results = get_elasticsearch_results(question)
context_prompt = create_openai_prompt(elasticsearch_results)
openai_completion = generate_openai_completion(context_prompt, question)
print(openai_completion)Tips for Using the Playground
- Ensure your index has the necessary mappings and data fields.
- Use filters and sorts to refine results for large datasets.
- Leverage the LLM’s natural language capabilities for easier query creation.
For more detailed guidance, refer to the official Elastic Playground Documentation
Conclusion
The Elasticsearch Playground is a powerful tool for querying and exploring datasets, such as international football results. It combines advanced search capabilities with modern AI, allowing for intuitive data interaction and conversational interfaces. Whether you are an analyst, developer, or researcher, the Playground offers new opportunities for data exploration and application development.
Dive into the Playground and explore your datasets like never before!
Feel Free to Reach Out at Linkedin:
#Elasticsearch #OpenAi #GenAi #Playground #Kibana #Gemini #RAG #LLM






Leave a comment