Exploring how Elastic Observability’s AI assistant enhances monitoring with detailed insight.

Observability provides detailed insights into the behavior of applications in your system, which is essential for identifying and resolving issues quickly. Elastic Observability combines logs, infrastructure metrics, application traces, user experience data, synthetics, and profiling into one integrated stack. Directly ingesting data into Elasticsearch enables data enrichment and processing, followed by powerful visualization and alerting capabilities through Kibana. This unified approach enhances system monitoring, helping teams quickly address performance bottlenecks and maintain smooth operations.
Observability AI Assistant
The AI assistant uses generative AI to provide:
- Contextual insights: Open prompts throughout Observability that explain errors and messages and suggest remediation.
- Chat: Engage in conversations with the AI Assistant. The chat function uses function calling to request, analyze, and visualize your data.
The AI assistant integrates with your large language model (LLM) provider through our supported Elastic connectors.
- OpenAI connector for OpenAI or Azure OpenAI Service.
- Amazon Bedrock connector for Amazon Bedrock.
Requirements
The AI assistant requires the following:
- Elastic Stack version 8.9 and later.
- An Enterprise subscription.
- An account with a third-party generative AI provider that supports function calling. The Observability AI Assistant supports the following providers.:
- OpenAI
gpt-4+. - Azure OpenAI Service
gpt-4(0613) orgpt-4-32k(0613) with API version2023-07-01-previewor more recent. - AWS Bedrock, specifically the Anthropic Claude models.
- The knowledge base requires a 4 GB machine learning node.
Set up the AI Assistant
To set up the AI Assistant:
- Create an authentication key with your AI provider to authenticate requests from the AI Assistant. You’ll use this in the next step. Refer to your provider’s documentation for information about creating authentication keys:
2. From Stack Management → Connectors in Kibana, create an OpenAI or Amazon Bedrock connector.
3. Authenticate communication between Observability and the AI provider by providing the following information:
In the URL field, enter the AI provider’s API endpoint URL.
Under Authentication, enter the API key or access key/secret you created in the previous step.
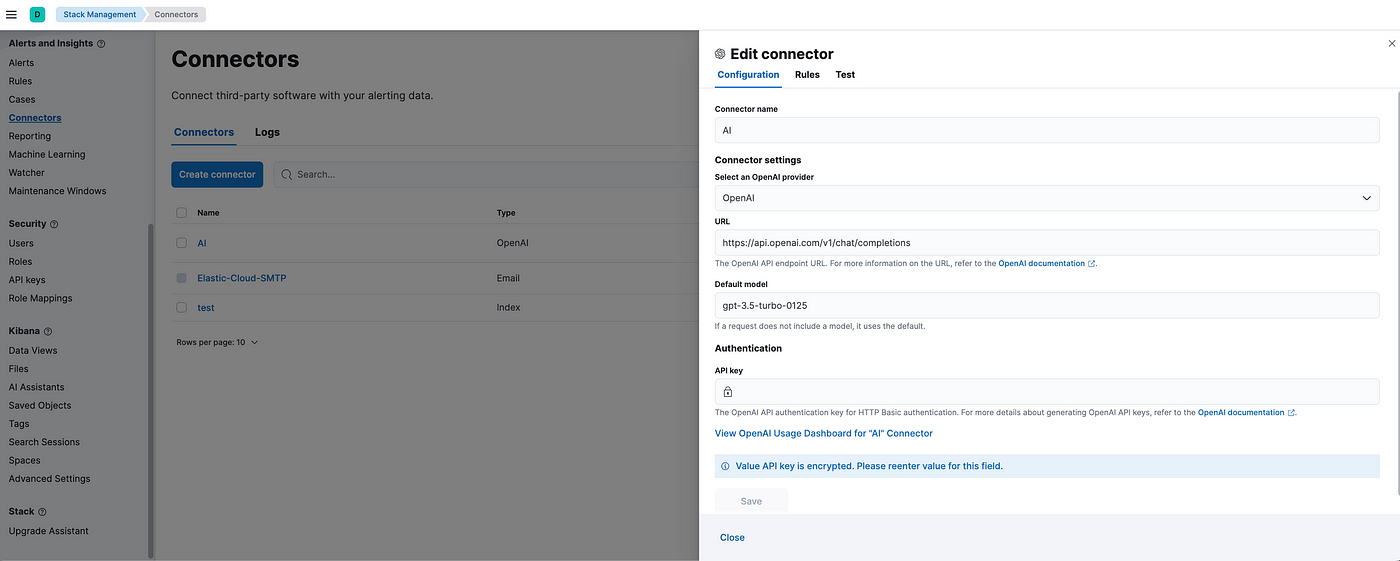

Test the connector after creating it to validate it’s working from the Test tab as in the above image.
Add data to the AI Assistant knowledge base
You can enhance the knowledge base by directing the AI Assistant to remember information during your conversation (e.g., “remember this for later”). The assistant will then summarize and store it. Additionally, you can incorporate external data into the knowledge base through Kibana’s Stack Management UI or the Elasticsearch Index API. This enables a more thorough and customizable information repository, facilitating improved insights and decision-making across your system.
To add external data to the knowledge base in Kibana:
- Go to Stack Management.
- In the Kibana section, click AI Assistants.
- Then select the Elastic AI Assistant for Observability.
- Switch to the Knowledge Base tab.
- Click the New entry button, and choose either:
- Single entry: Write content for a single entry in the UI.
- Bulk import: Upload a newline delimited JSON (
ndjson) file containing a list of entries to add to the knowledge base.

Users can chat with the AI assistant or interact with contextual insights in Observability under all the sections.
Start the AI Assistant
Click AI Assistant in the upper-right corner of any Observability application to initiate the chat.
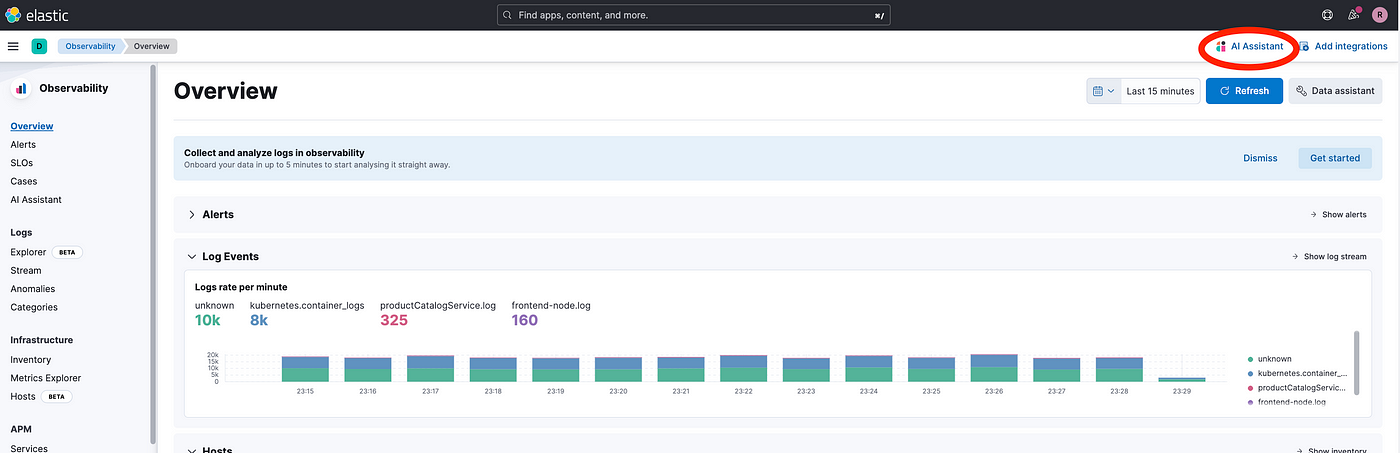

There are built-in functions available for users to better utilize AI Assistant prompts. The AI Assistant uses functions to include relevant context in the chat conversation through text, data, and visual components.
Now from the Observability home page in AI Assistant, Type something like ‘Explain this section’. The AI assistant will explain the current details.

Using Smart Prompts
Users can now interact with the AI assistant in each section by asking relevant questions and then continuing the discussion as desired.
Examples of detailed interaction with AI Assitant in the APM section to understand the capability of Elastic Observability AI Assitant:
- Application performance monitoring (APM) — Identify the service with most failed transactions

Prompt: List and explain all the transactions of frontend-otel service in the last 2 hours.

As part of our ongoing conversation, I requested the AI assistant to list the total number of POST requests for these services in the last hour. I received the following response, which provided me with the total count.

Few More Interesting prompts and conversations:
Prompt: What are the data sources for the frontend-otel service and languages and are details on the agent?

Prompt: What are the dependencies for this service and are there any errors in the last 24 hours if yes explain the error and how to resolve them.

As shown in the screenshot above, the AI Assistant has effectively summarized the entire request and provided an in-depth analysis. This can be further adjusted and improved based on our input and additional interactions.
Now Let’s investigate a bit more in depth one of the errors with the help of AI Assistant and see what it comes up with.
Prompt: Do you have more insight and detail on the error “13 INTERNAL: failed to prepare order: failed to get product #OLJCESPC7Z” and resolution?
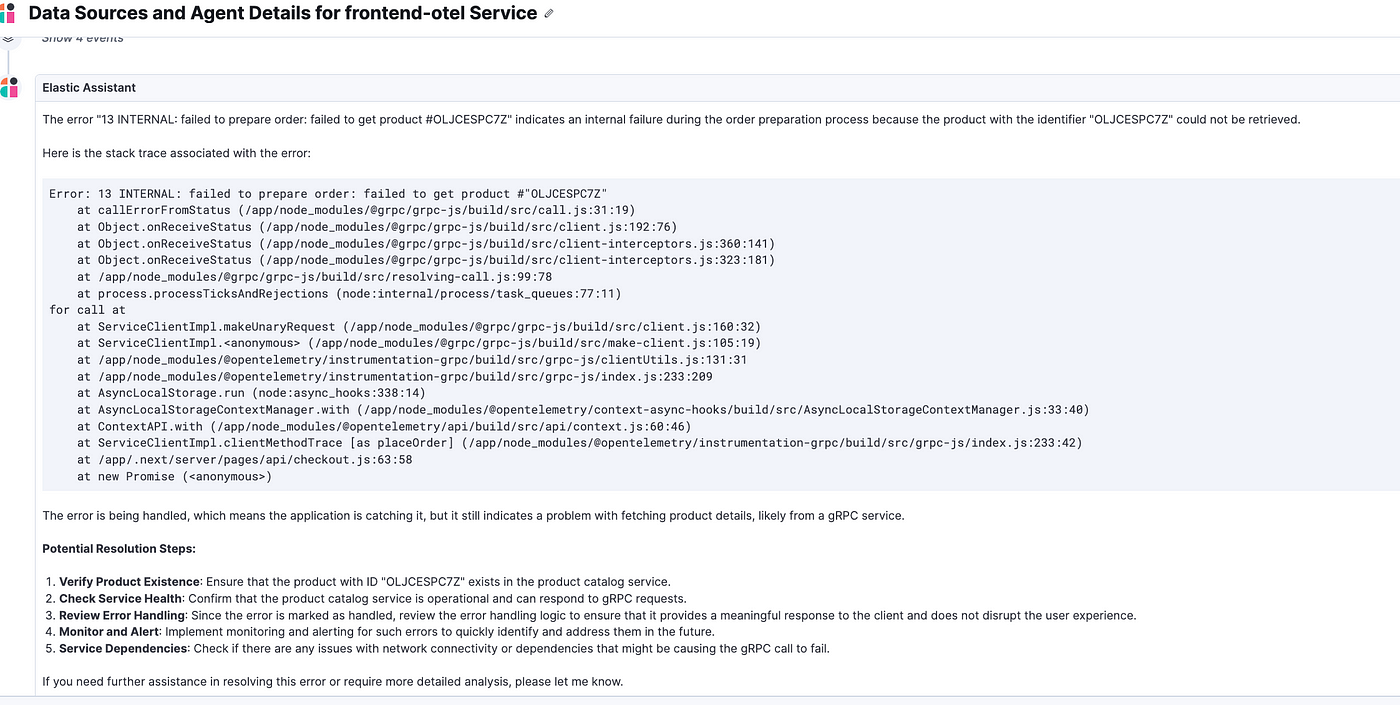
Now I tried setting up an alert on any further error on this service while continuing my interaction to see if that works.
Prompt: Set an alert for any further error on this service
Even though the AI assistant didn’t set it, it is giving me steps to do so which is good.

As a next step, I want to understand the service map and analyze the specific APM service to see what I can get from the tool.
Prompt: Explain and analyze the service map of frontend-otel service.

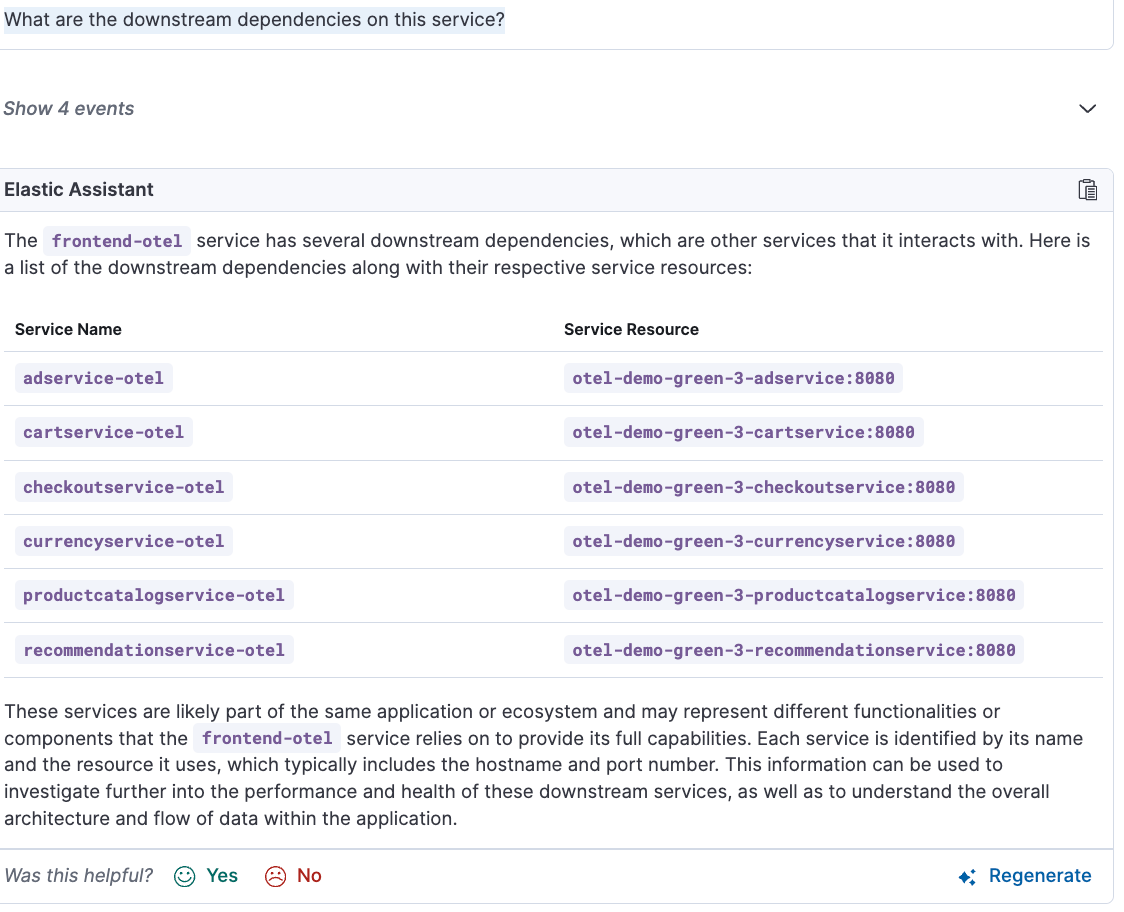
Now let’s take a deeper dive into the downstream dependencies of this frontend-otel service.
Prompt: What are the downstream dependencies on this service?
- Logs
Prompt: Find all errors in the last 24 hours and summarize them.
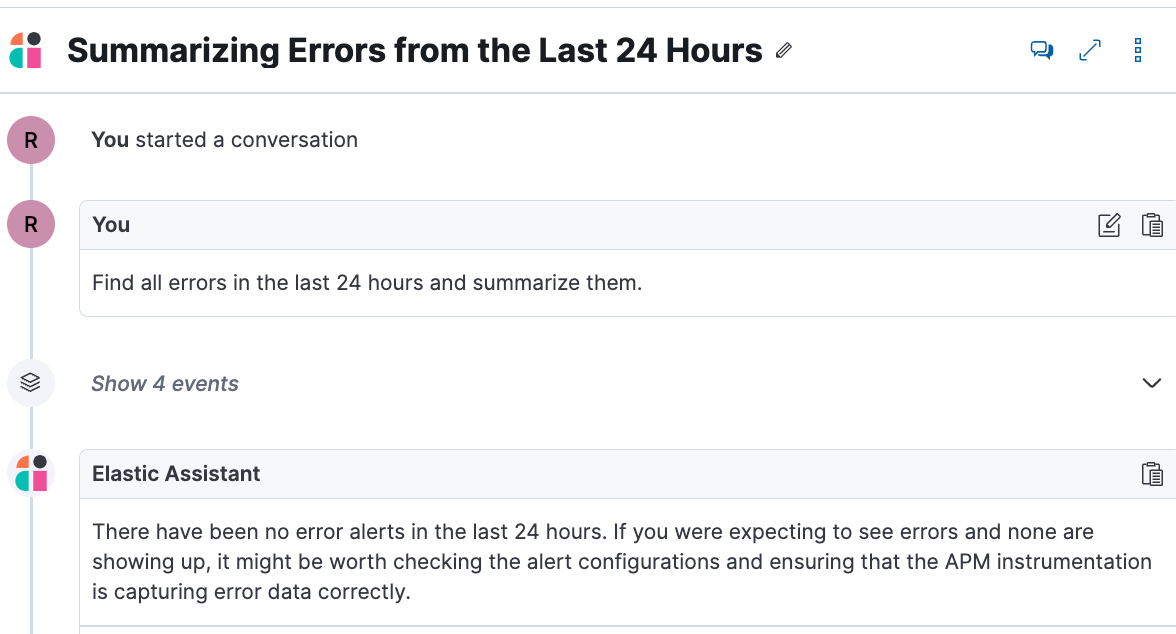
Next, Click on a log message and Ask the AI assistant “What’s this message”.

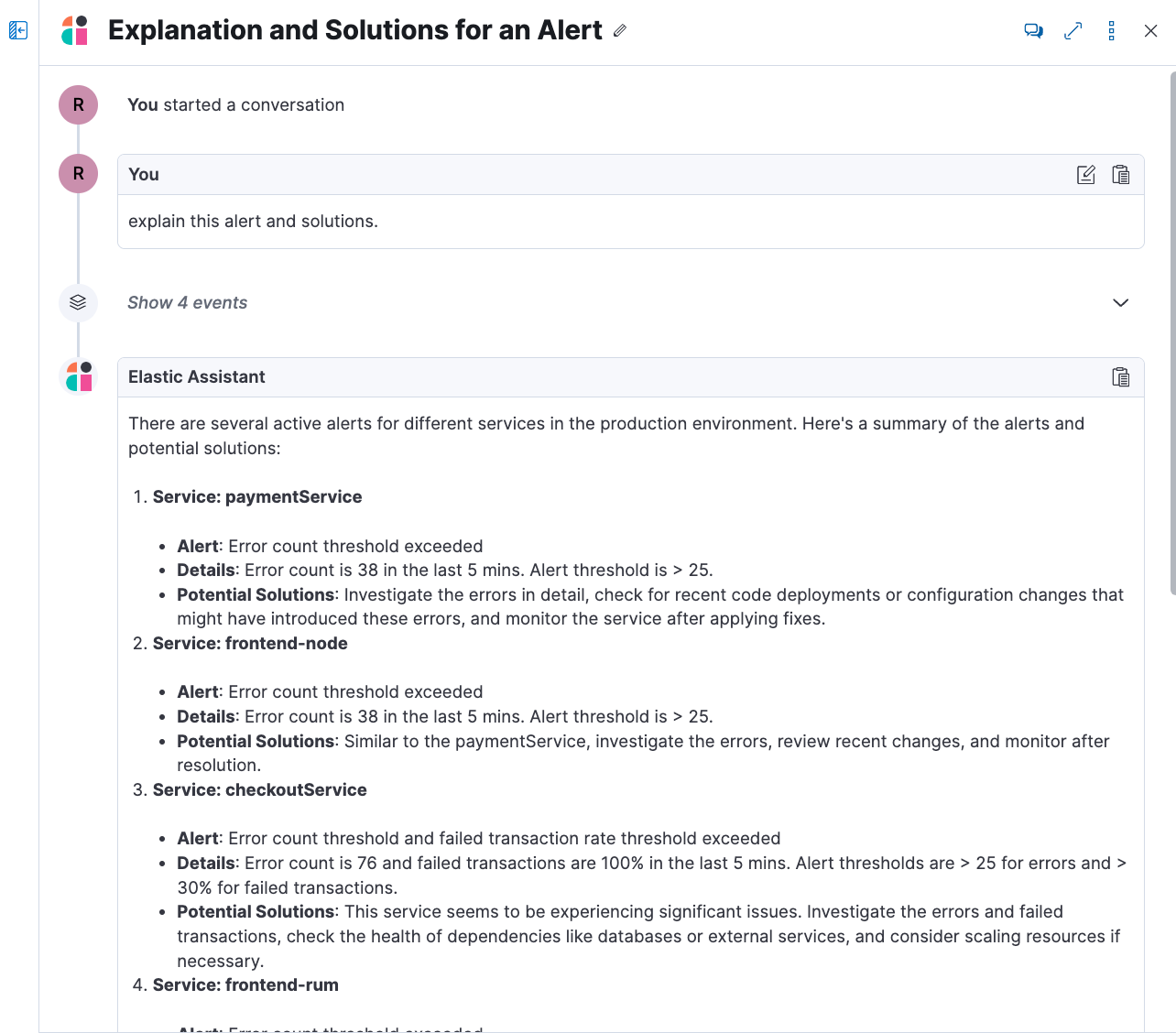
- Alerting
Prompt: explain this alert and solutions.

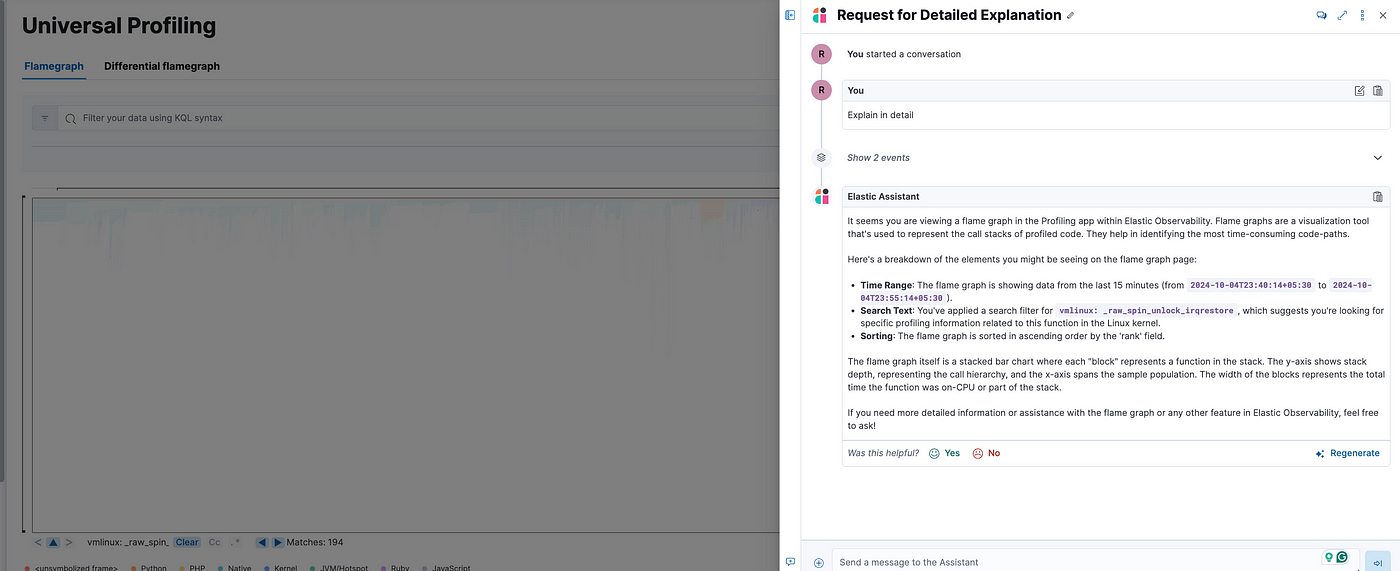
- Universal Profiling
Prompt: explains the most expensive libraries and functions on this page and shares optimization suggestions.

Infrastructure Observability
Prompt: explain and summarize the inventory page

Synthetic Monitor
Prompt: Which service has been down in the last 24 hours?

Now click on any one of the uptime services to investigate further.
Prompt: Summarize the uptime status of this service and share a detailed report
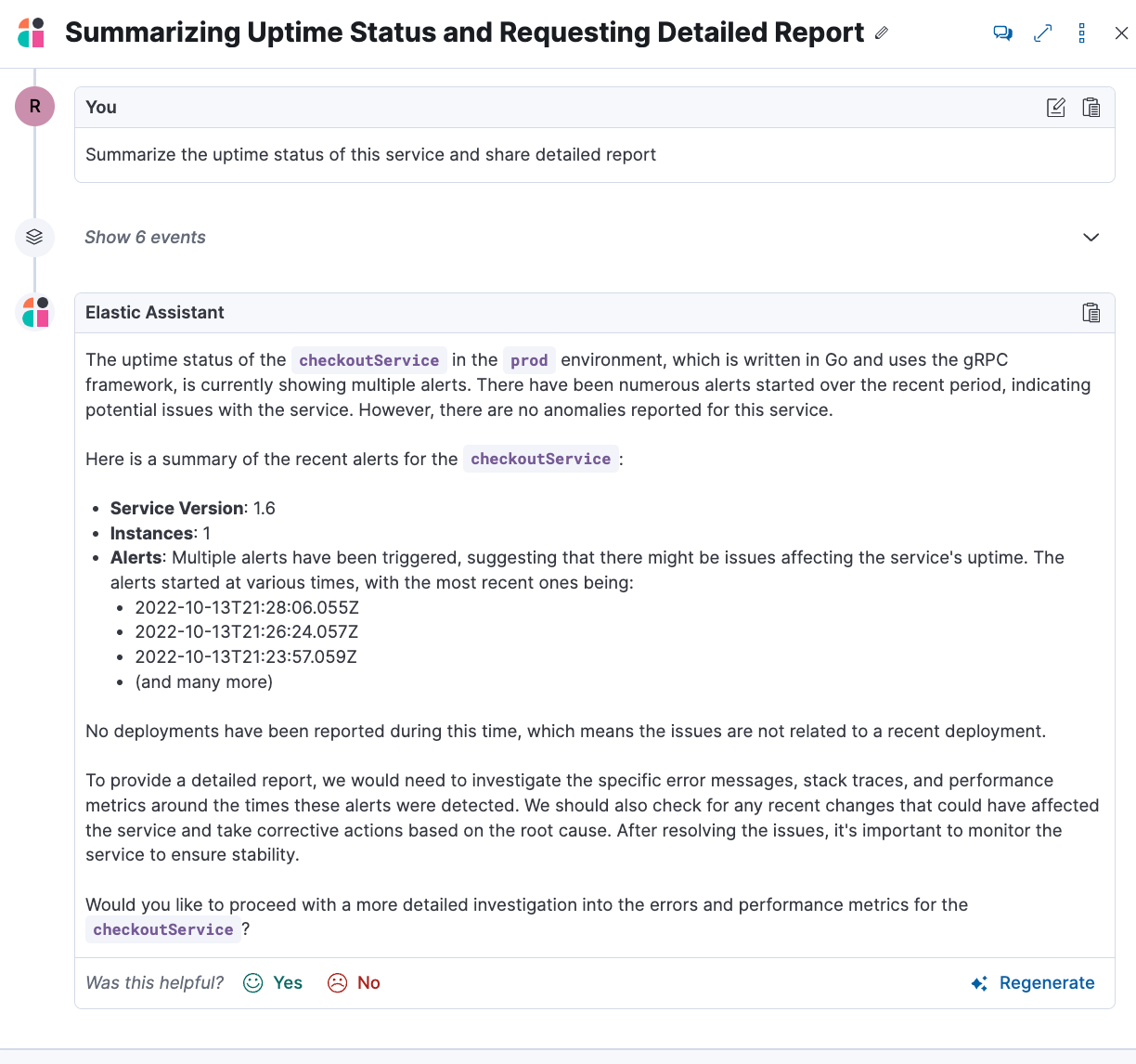
Now let’s do a detailed investigation of the service by continuing the conversation:
Prompt: Yes do a detailed investigation.

As seen in the image above, the level of detail demonstrates the power of Observability AI Assistant. It can be incredibly helpful during investigations, issue resolution, and normal operations.
Errors due to LLM token limit:
Most LLMs have a set limit of tokens they can handle in a single conversation. When you reach the token limit, the LLM will throw an error, and Elastic will display a “Token limit reached” error in Kibana.
Or you may encounter the following error, which is again due to issues with the OpenAI subscription. You will essentially need a premium subscription to freely experiment and avoid reaching limits.
Status code: 429. Message: API Error: Too Many Requests - You exceeded your current quota, please check your plan and billing details. For more information on this error, read the docs: https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/error-codes/api-errors.Don’t miss to try out the Elastic AI Assistant with a knowledge base containing your data.
I encourage all readers to experiment with their prompts and share their findings as comments. We can learn from each other.
Related Article:
OpenTelemetry with Elastic Observability
Elastic RUM (Real User Monitoring) with Open Telemetry (OTel).
OpenTelemetry: Automatic vs. Manual Instrumentation — Which One Should You Use?
Configuration of the Elastic Distribution of OpenTelemetry Collector (EDOT)
Test and Analyze OpenTelemetry Collector processing
Why Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Is Not Just Vector Search, but a Lot More
#otel #docker #kubernetes #devops #elasticsearch #observability #search #apm #APM #grafana #datadog #ebpf #UniversalProfiling
Feel Free to Reach Out at Linkedin:





Leave a comment